Java输入输出流
一. File类
1.1 概述
- 什么是文件?
- 文件可认为是相关记录或放在一起的数据的集合
- 在Java中,使用java.io.File类对文件进行操作
1.2 文件操作
-
创建File对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8//方式一(全路径)
//File file1 = new File("h:\\BA_NANA\\io\\myFile.txt");
//方式二(父路径+子路径)
//File file1 = new File("h:\\BA_NANA","io\\myFile.txt");
//方式三(file对象路径+子路径)
File file = new File("h:\\BA_NANA");
File file1 = new File(file,"io\\myFile.txt"); -
判断是否为文件或目录
1
2
3
4
5//返回值为boolean类型
System.out.println("是否为文件夹:" + file1.isDirectory());
System.out.println("是否为文件:" + file1.isFile());
//若文件夹或文件不存在一致返回false -
创建文件夹
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8File file2 = new File("h:\\BA_NANA\\bulid\\pics");
if(!file2.exists()){ //若文件夹不存在则创建
//只创建子目录(pics),若父目录不存在(返回false)则不会创建
file2.mkdir();
//若父目录不存在,创建父目录再创建子目录(返回true)
file2.mkdirs();
} -
创建文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10File file1 = new File("h:\\BA_NANA","io\\test.txt");
//若文件不存在,则创建文件
if(!file1.exists()){
try {
file1.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
二. 字节流和字符流
2.1 字节流
-
字节输入流 InputStream
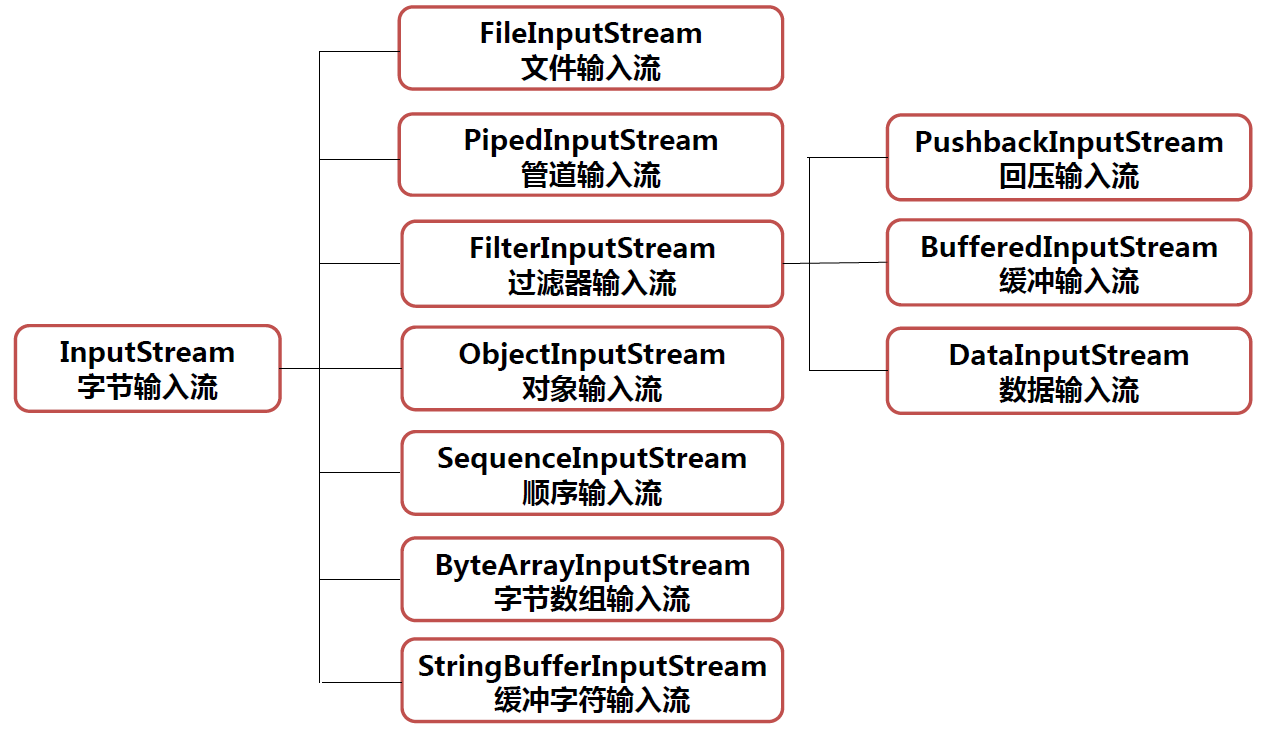
-
字节输出流 OutputStream
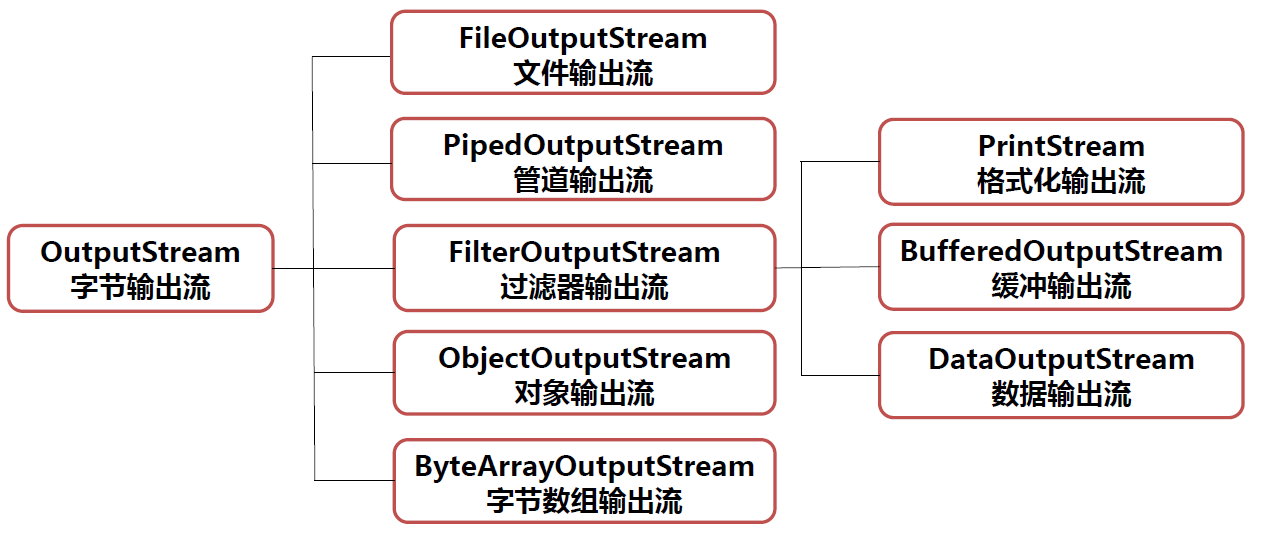
2.2 FileInputStream
-
从文件系统中某个文件获得输入字节
-
用于读取如图像数据的原始字节流
-
常用方法
方法名 描述 public int read() 从输入流中读取一个数据字节 public int read(byte[] b) 从输入流中将最多b.length个字节的数据读入一个byte数组中 public int read(byte[] b,int off,int len) 从输入流中将最多len个字节的数据读入byte数组中 public void close() 关闭此文件输入流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源 -
read方法返回-1,则表示已读到文件末尾
-
代码案例一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21//方法一 read()
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个FileInputStream对象
{
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
int n=0;
while ((n=fis.read())!=-1){
//返回ASCII码,到末尾返回-1
System.out.print((char)n);
}
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} -
代码案例二
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16//方法二 read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
//创建字符数组
byte[] b = new byte[100];
//读取数据存入字符数组中,off为数组偏移量,len为读取数据的长度
fis.read(b,0,5);
System.out.println(new String(b));
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}除了上述两种方法可以读取文件内容,还可以参考后面的补充方法。
2.3 FileOutputStream
-
常用方法
方法名 描述 public void write(int b) 将指定字节写入此文件输出流 public void write(byte[] b) 将b.length个字节从byte数组写入文件输出流 public void write(byte[] b,int off,int len) 将byte数组中偏移量为off开始的len个字节写入文件输出流 public void close() 关闭此文件输入流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源 -
代码案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19//基本的写入数据到文件中
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("test.txt",true);//true代表添加数据到文件末尾,而不是覆盖文件数据
fos.write(50); //在文件中并没有显示50,因此字节流不适合存储阅读文本,适合存储图像等数据
fos.write('a');
System.out.println(fis.read());
System.out.println((char)fis.read());
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
} -
代码案例(复制图片)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public static void main(String[] args) {
//文件拷贝
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("logo.png");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("logocopy.jpg");
int n=0;
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
//未解决疑惑:n如果代表一段长度,为什么char(n)可以转换成字符呢?
while ((n=fis.read(b))!=-1){
fos.write(b,0,n);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2.4 缓冲流
-
缓冲输入流 BufferedInputStream
-
缓冲输出流 BufferedOutputStream
-
代码案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
bos.write(50);
bos.write('a');
//缓冲区不满,要调用flush方法或close方法强制清空或才会输出到文件
bos.flush();
System.out.println(bis.read());
System.out.println((char)bis.read());
//判断时间差,是否缓冲流能提高输入输出速度?
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime-startTime);
fos.close();
fis.close();
bos.close();
bis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2.5 字符流
-
字符输入流 Reader
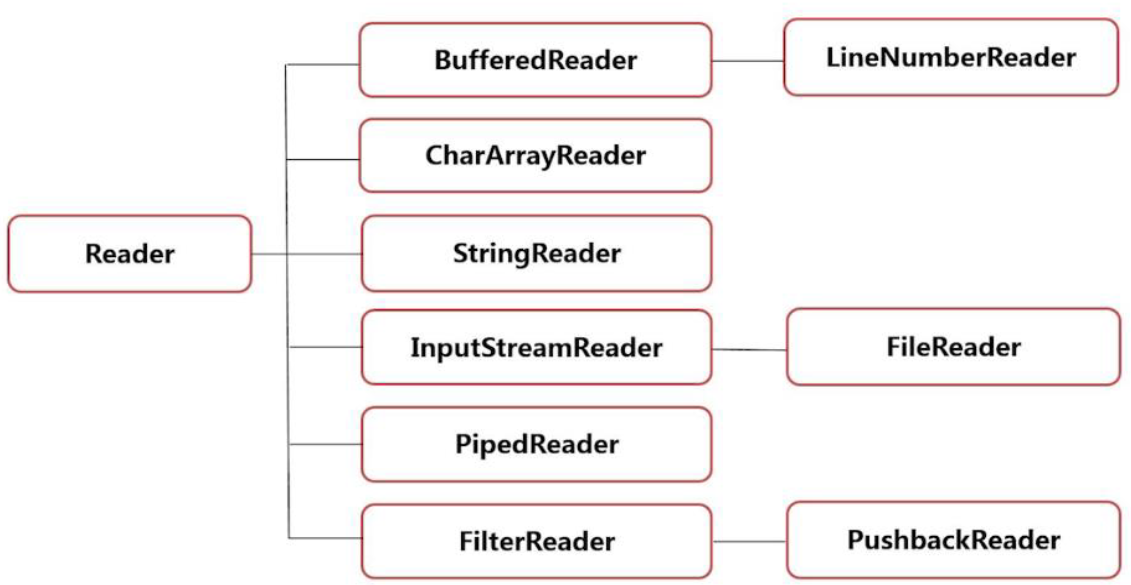
-
字符输出流 Writer
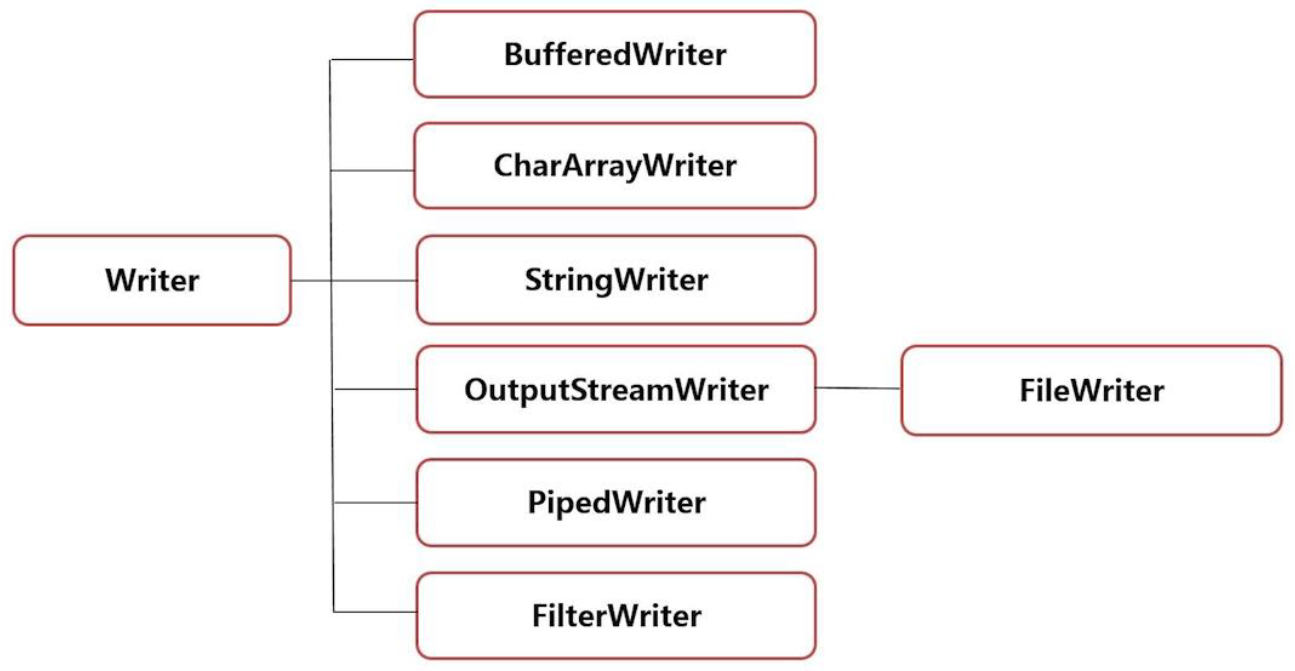
-
适用于输入输出字符
2.6 字节字符转换流
-
InputStreamReader
-
OutputStreamWriter
-
代码案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//创建文件输入输出流,再创建字节字符转换流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
//将字节输入流转换为字符输入流,并指定编码格式
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"GBK");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test1.txt");
//将字符输出流转换为字节输出流,并指定编码格式
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"GBK");
//注意在字符字节转换流中编码格式要统一,默认或者设置为同一个编码格式
int n=0;
char[] cbuf = new char[10]; //这里是char不是byte
// while ((n=isr.read())!=-1){
// System.out.print((char)n);
// }
while((n=isr.read(cbuf))!=-1){
//将字符转换为字符串
String s = new String(cbuf,0,n);
osw.write(s);
osw.flush();
}
//关闭流
fis.close();
fos.close();
isr.close();
osw.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2.7 读取文件方法补充
-
示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15/*2020-10-25*/
public class ProblemSecond {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 从文件读取不同字符串
File file = new File("test.txt");
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
String line = "";
while((line = reader.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
}
}
三. 对象的序列化和反序列化
-
序列化:把Java对象转换为字节序列的过程
-
反序列化:把字节序列恢复为Java对象的过程
-
对象输入流 ObjectInputStream
-
对象输出流 ObjectOutputStream
-
代码案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义Goods类对象,该对象要实现Serializable接口
Goods goods1 = new Goods("20190001","华为Mate30","3999");
try {
//将对象信息写入文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(goods1);
//读对象信息
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
try {
Goods goods2 = (Goods)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(goods2);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
oos.flush();
fos.close();
oos.close();
fis.close();
ois.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
} -
更多关于输入输出流的使用参考Java api文档中的java.io部分
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 515code-实验室!
评论